Main features of Medical Tourism in 21st Century:
- Large numbers of patients travelling for treatment
- Patients from developed and rich nations travelling to developing countries to avail good quality treatment at low-cost, aided by cheap air travels and internet as a means of quick information
- Excellent infrastructure that is easily accessible and affordable
- Medical tourism has become a profitable source of foreign revenue and is being promoted by both the national government and private business sectors of developing and developed nations equally
THE MEDICAL TOURISM MARKET
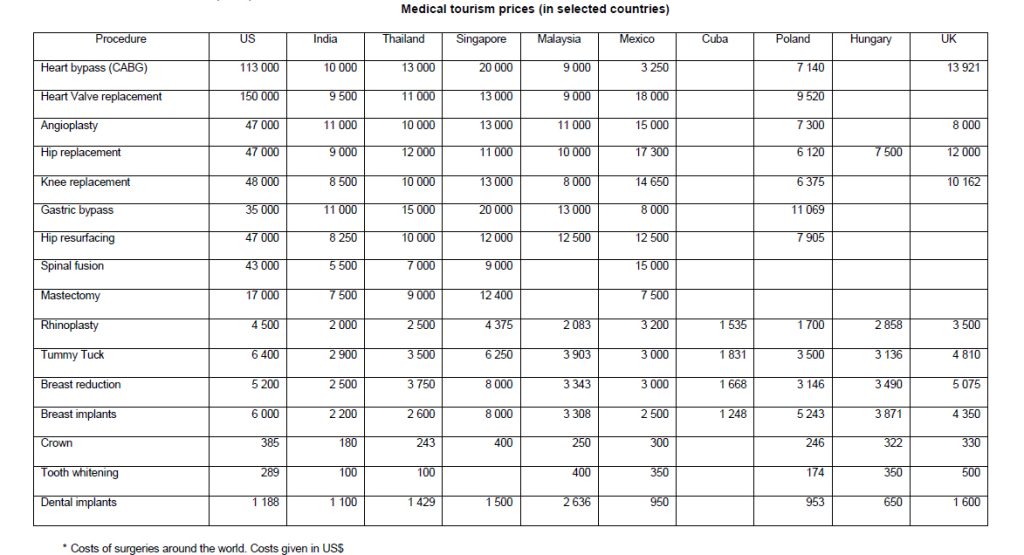
There is a wide range of health services and treatments available for overseas medical tourists. Some of the services that are commonly used are as follows:
- Dentistry (cosmetic and reconstruction)
- Cardiology / cardiac surgery (by-pass, valve replacement)
- Bariatric surgery (gastric by-pass)
- Orthopaedic surgery (hip replacement, joint surgery, resurfacing, and knee replacement)
- Organ, cell and tissue transplantation
- Fertility / reproductive system (IVF and gender reassignment)
- Eye surgery
- Cosmetic surgery (face, breast, and liposuction)
- Diagnostics and check-ups
Furthermore, while some of these treatments are for acute and life-threatening illnesses, some are secondary and more mainstream healthcare. There are some forms of cosmetic surgery that would not be included in health spending, while others such as IVF would be counted within the remit of health trade (OECD, 2010).
NOTE:
Moreover, in order to cater to the rising medical tourists (Chinai and Goswami, 2007) and to allow tax breaks to the providers, India has introduced a special visa category, an ‘M visa’. According to Sengupta (2008), medical tourism facilities increase the depreciation on life saving equipments and also land at subsidised rates.
TREATMENT PROCESSES
The treatment processes ensure the following:
- Quality and safety
- Risk minimization
- Patient satisfaction
- Clinical outcomes
- Continuity of care
- Privacy and confidentiality
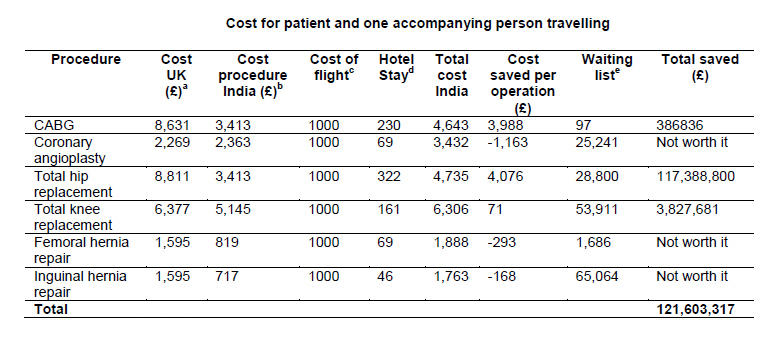
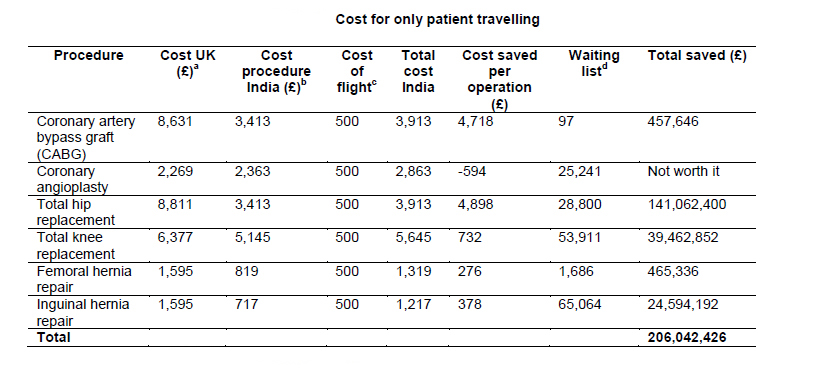
In fact, the main ingredients for according safer and better health care services for domestic consumption and medical travelers are quality maximization and risk minimization. This can be achieved only with the help of appropriate forms of organizational framework within the hospital or healthcare centre designed to check quality, ascertain risk, and consideration of all relevant issues, and maintaining vigilance. Currently, medical tourism services are mostly unregulated and an important factor to consider is the trustworthiness of the safety and quality standards offered by medical tourism.